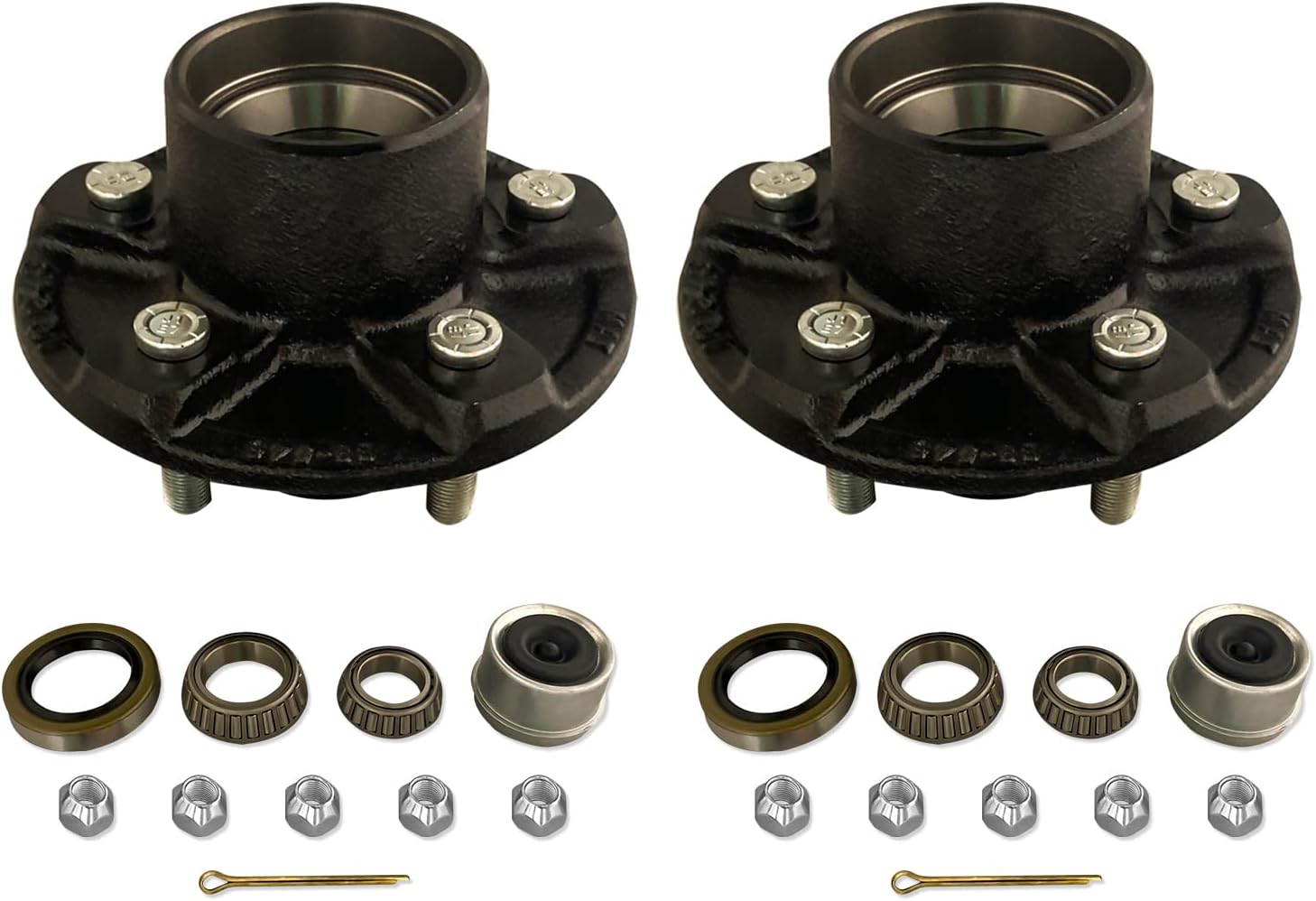
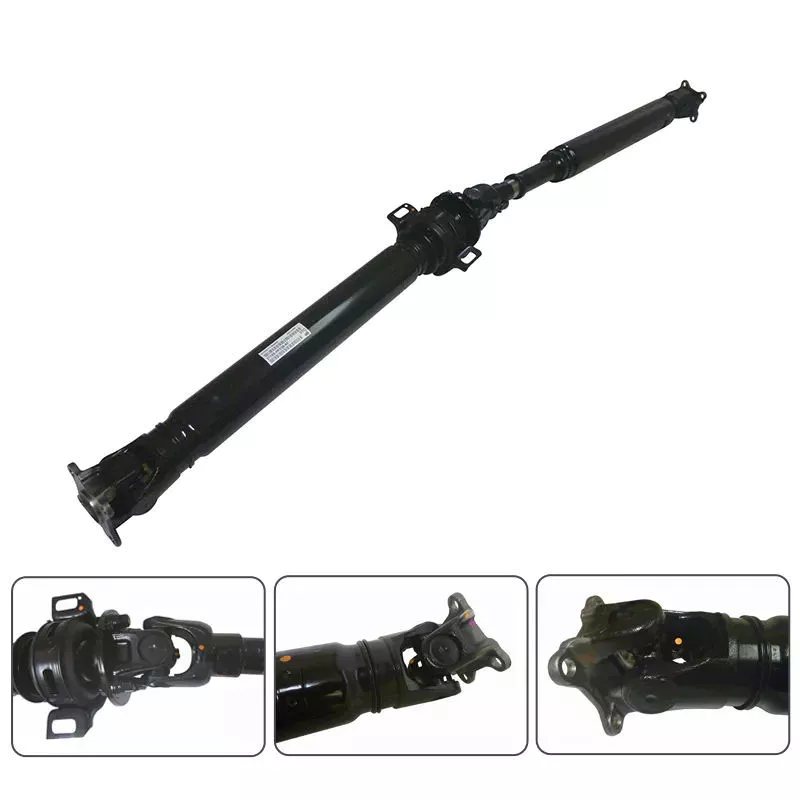
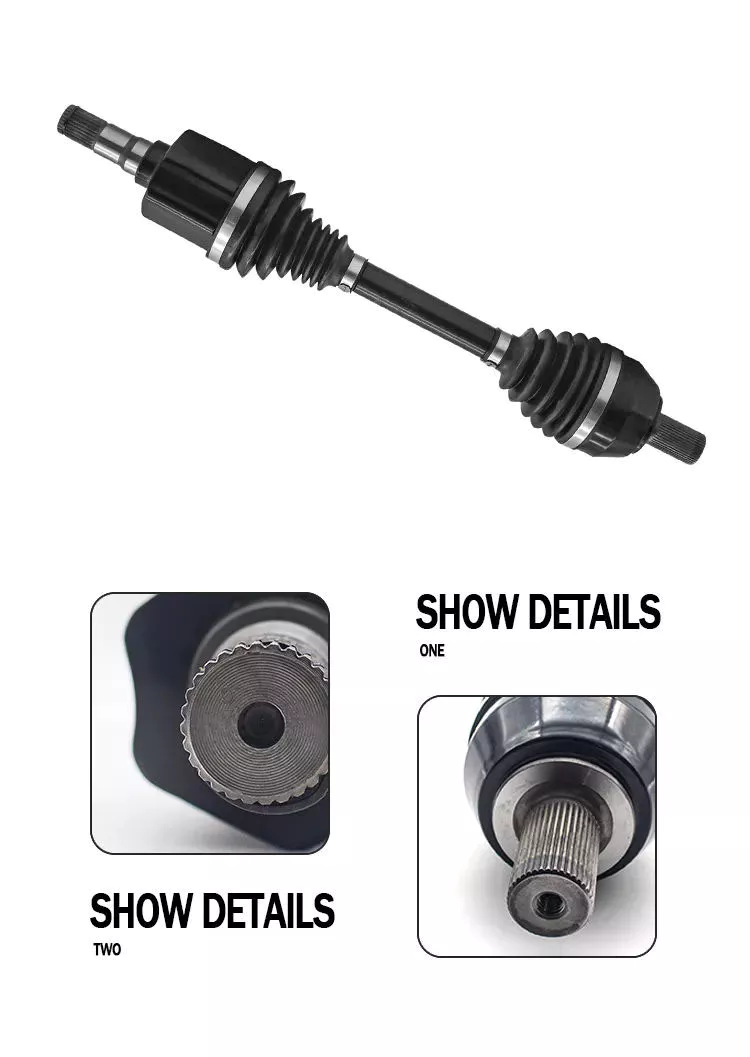
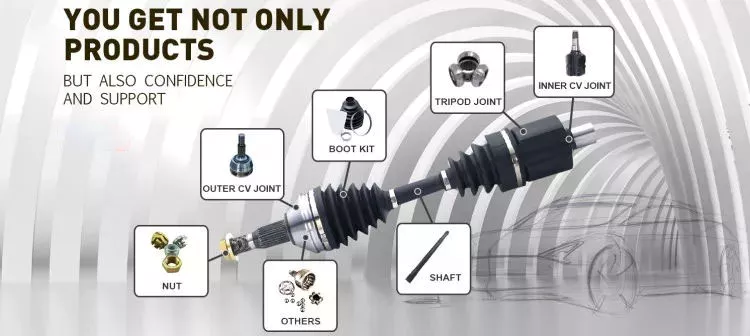
Product Description
OEM Front Side Automobile Axle Bearing Wheel Bearing Wheel Hub
Product Description
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Specifications
1.Supply to USA, Europe, and Australia
2.Material:40Cr/ 4130 Heat Treated Chromoly Steel/ 4340 Heat Treated Chromoly Steel/ 300M
3.Surface: Sand Blast/ Silver Zinc/ Yellow Zinc/ Black Zinc/ Chrome Finish/ Electrophoresis
We could manufacture all kinds of wheel hub assembly according to OEM No., Your Samples, or Drawings.
Bearings are usually installed to carry equipment on the shaft. The hardness and adhesion of the material itself buffer the impact of the bearing on the shaft head and reduce the appearance of the shaft head and hub wear.
Surface Treatment:
High quality stainless steel metal with high gloss and corrosion resistance. We guarantee the density of the liquid metal and the strength of the solidified metal.
Material Selection:
Ensure the strength of metal solidification, thick hub, hub uniform, not easy to break, more durable.
1) Don’t do the best, just do better
2) Quality:Using high-quality raw materials and innovative technology can make your product quality better and more Stable.And enhance market competitiveness
3) Quick Q&A that might save some of your concerns. Sincerity: We are committed to providing high quality products and services.There is no fake and no cheat Experience: We always focus on Technology and Quality,So we got rich professional experiences and had an excellent technical team. Services: We can offer fast pruducting and fast delivery and customized products,With a good after-sales services Win-Win: With a large number of satisfied customers in China.We are looking forward to meet you from all over the world Mission: To deliver high quality and reasonable products to customers all around the world.
Q1:Are you a manufacturer or a trading company?
We are both a factory and a trading company. This type can meet our customers’ requirements for flexible export. We are manufacturers, and our quality and price will be competitive in the market. In addition, we also have professional sales teams and engineers to provide you with the greatest support.
Q2:Why should we buy from your company instead of other suppliers?
We maintain good quality and competitive prices to ensure that our customers benefit. All our products are 100% tested before shipment. We take the initiative to provide you with better, more efficient, and more reliable solutions
Q3:Do you provide OEM/ODM services?
We have an experienced R&D team, advanced equipment, and a quality control laboratory factory. Of course, we can provide OEM/ODM services.
Q4:How to customize (OEM/ODM)?
If you have new product drawings or samples, please send them to us, and we can customize the hardware according to your requirements. We will also provide our professional suggestions on products to make the design more realized and maximize performance.
Quality First, Price Best, Service Foremost!
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | as Specification |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | as Specification |
| Certification: | DOT |
| Samples: |
US$ 5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
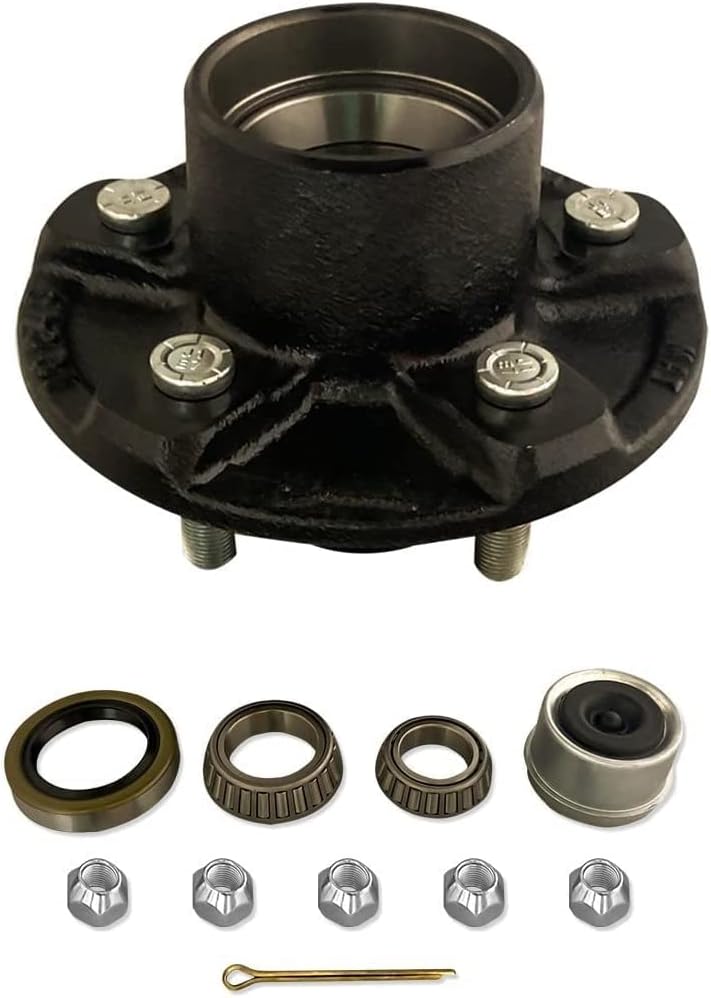

What are the common symptoms of a failing axle hub, and how can they be identified?
Identifying the common symptoms of a failing axle hub is crucial for timely diagnosis and repair. Here’s a detailed explanation of the common symptoms and how they can be identified:
1. Wheel Vibrations:
One of the common symptoms of a failing axle hub is noticeable wheel vibrations. As the hub becomes worn or damaged, it may cause the wheel to wobble or shake while driving. These vibrations can be felt through the steering wheel, floorboard, or seat. To identify this symptom, pay attention to any unusual vibrations that occur, especially at higher speeds.
2. Grinding or Growling Noises:
A failing axle hub can produce grinding or growling noises. This can be an indication of worn-out or damaged wheel bearings within the hub. The noise may vary in intensity, and it is often more pronounced during turns or when the vehicle is in motion. To identify this symptom, listen for any unusual grinding or growling sounds coming from the wheels while driving.
3. Wheel Play or Looseness:
A failing axle hub can result in wheel play or looseness. When the hub is damaged or worn, it may not provide a secure mounting point for the wheel. As a result, the wheel may have excessive play or feel loose when you attempt to wiggle it by hand. To identify this symptom, jack up the vehicle and try to move the wheel in different directions to check for any abnormal movement.
4. Uneven Tire Wear:
A failing axle hub can contribute to uneven tire wear. If the hub is damaged, it can affect the alignment and cause the tire to wear unevenly. Look for signs of abnormal tire wear, such as excessive wear on one side of the tire or feathering patterns. Uneven tire wear may also be accompanied by other symptoms, such as vibrations or pulling to one side while driving.
5. ABS Warning Light:
In some cases, a failing axle hub can trigger the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) warning light on the vehicle’s dashboard. This can occur if there is a problem with the wheel speed sensor, which is often integrated into the hub assembly. The ABS warning light indicates a fault in the braking system and should be diagnosed using a diagnostic tool by a qualified technician.
6. Visual Inspection:
A visual inspection can also help identify signs of a failing axle hub. Look for any visible damage or wear on the hub, such as cracks, corrosion, or bent flanges. Additionally, check for any leaking grease around the hub or signs of excessive heat, which can indicate bearing failure.
7. Professional Diagnosis:
If you suspect a failing axle hub but are unsure, it is recommended to have the vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic. They can perform a comprehensive examination of the wheel assembly, including the hub, bearings, and associated components. They may use specialized tools and equipment to measure wheel play, check for bearing wear, and assess the overall condition of the hub.
In summary, common symptoms of a failing axle hub include wheel vibrations, grinding or growling noises, wheel play or looseness, uneven tire wear, ABS warning light activation, and visible damage. It is essential to pay attention to these symptoms and seek professional diagnosis and repair to prevent further damage and ensure the safe operation of the vehicle.
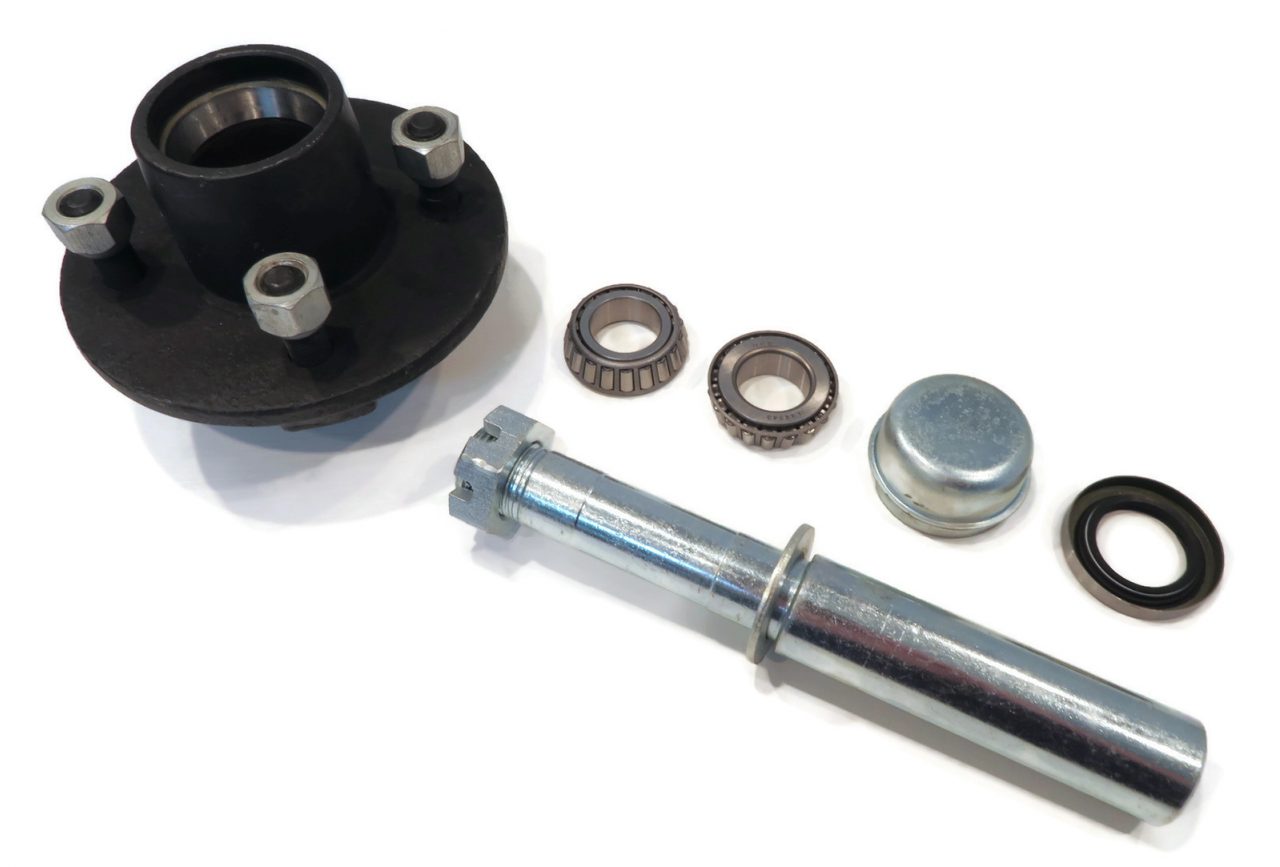

How often should axle hubs be inspected and replaced as part of routine vehicle maintenance?
Regular inspection and maintenance of axle hubs are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a vehicle. The frequency of inspection and replacement may vary depending on several factors, including the vehicle’s make and model, driving conditions, and manufacturer’s recommendations. Here are some guidelines to consider:
- Manufacturer’s recommendations: The first and most reliable source of information regarding the inspection and replacement intervals for axle hubs is the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations. These can usually be found in the owner’s manual or the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule. It is essential to follow these guidelines as they are specific to your particular vehicle.
- Driving conditions: If your vehicle is subjected to severe driving conditions, such as frequent towing, off-road use, or driving in extreme temperatures, the axle hubs may experience increased stress and wear. In such cases, more frequent inspections and maintenance may be necessary.
- Visual inspection: It is a good practice to visually inspect the axle hubs during routine maintenance or when performing other maintenance tasks, such as changing the brakes or rotating the tires. Look for any signs of damage, such as leaks, excessive play, or worn-out components. If any abnormalities are detected, further inspection or replacement may be required.
- Wheel bearing maintenance: The axle hubs house the wheel bearings, which are critical for the smooth rotation of the wheels. Some vehicles have serviceable wheel bearings that require periodic maintenance, such as cleaning and repacking with fresh grease. If your vehicle has serviceable wheel bearings, refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate maintenance intervals.
- Unusual noises or vibrations: If you notice any unusual noises, such as grinding, humming, or clicking sounds coming from the wheels, or if you experience vibrations while driving, it could be an indication of a problem with the axle hubs. In such cases, immediate inspection and necessary repairs or replacement should be performed.
It’s important to note that the intervals for inspecting and replacing axle hubs can vary significantly between different vehicles. Therefore, it is recommended to consult the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations to determine the specific maintenance schedule for your vehicle. Additionally, if you are unsure or suspect any issues with the axle hubs, it is advisable to have a qualified mechanic or automotive technician inspect and assess the condition of the axle hubs.
In summary, the frequency of inspecting and replacing axle hubs as part of routine vehicle maintenance depends on factors such as the manufacturer’s recommendations, driving conditions, visual inspections, wheel bearing maintenance requirements, and the presence of any unusual noises or vibrations. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and promptly addressing any abnormalities will help ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the axle hubs.

Can axle hubs impact the alignment of a vehicle, and how is this corrected?
Axle hubs can indeed impact the alignment of a vehicle, and any alignment issues arising from the axle hubs should be corrected to ensure optimal vehicle handling, tire wear, and overall safety. Here’s a detailed explanation:
An axle hub is a critical component that connects the wheel assembly to the vehicle’s suspension. It houses the wheel bearings and provides the mounting point for the wheel. If an axle hub is damaged, worn, or improperly installed, it can lead to misalignment issues. Here are a few ways axle hubs can impact vehicle alignment:
- Bearing Wear: Axle hubs contain wheel bearings that allow the wheels to rotate smoothly. If the bearings are worn or damaged, they can introduce play or uneven movement in the wheel assembly. This can result in misalignment, causing the vehicle to pull to one side or affect the camber, toe, or caster angles.
- Improper Installation: If an axle hub is not installed correctly, it can introduce misalignment issues. For example, if the hub is not tightened to the specified torque or if the mounting surfaces are not properly cleaned, it can result in uneven pressure distribution and misalignment.
- Impact Damage: Axle hubs can get damaged due to accidents, hitting potholes, or other impacts. Any deformation or misalignment of the axle hub can affect the alignment of the wheel assembly.
To correct alignment issues caused by axle hubs, the following steps are typically taken:
- Inspection: A thorough inspection of the axle hubs is conducted to identify any damage, wear, or improper installation. This may involve removing the wheels and visually examining the axle hubs for signs of damage or wear.
- Replacement: If the axle hubs are found to be damaged, worn, or improperly installed, they need to be replaced. Replacement axle hubs should be sourced from reputable manufacturers or OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) suppliers to ensure proper fit and alignment.
- Wheel Alignment: After replacing the axle hubs, a wheel alignment procedure is necessary to correct any misalignment caused by the previous issues. This typically involves adjusting the camber, toe, and caster angles to the manufacturer’s specifications using specialized alignment equipment.
- Additional Repairs: In some cases, axle hub-related alignment issues may have caused additional damage to suspension components or steering linkage. These components should be inspected and repaired as needed to ensure proper alignment and functionality.
It’s important to note that correcting alignment issues caused by axle hubs generally requires the expertise of a qualified mechanic or alignment specialist. They have the necessary knowledge, experience, and equipment to accurately diagnose and rectify alignment problems associated with axle hubs.
In summary, axle hubs can impact the alignment of a vehicle. Issues such as bearing wear, improper installation, or impact damage can introduce misalignment. To correct these alignment issues, a thorough inspection of the axle hubs is conducted, followed by replacement if necessary. Afterward, a wheel alignment procedure is performed to adjust the angles to the manufacturer’s specifications. Professional assistance from a qualified mechanic or alignment specialist is recommended to ensure accurate diagnosis and proper correction of axle hub-related alignment issues.


editor by CX 2024-04-23
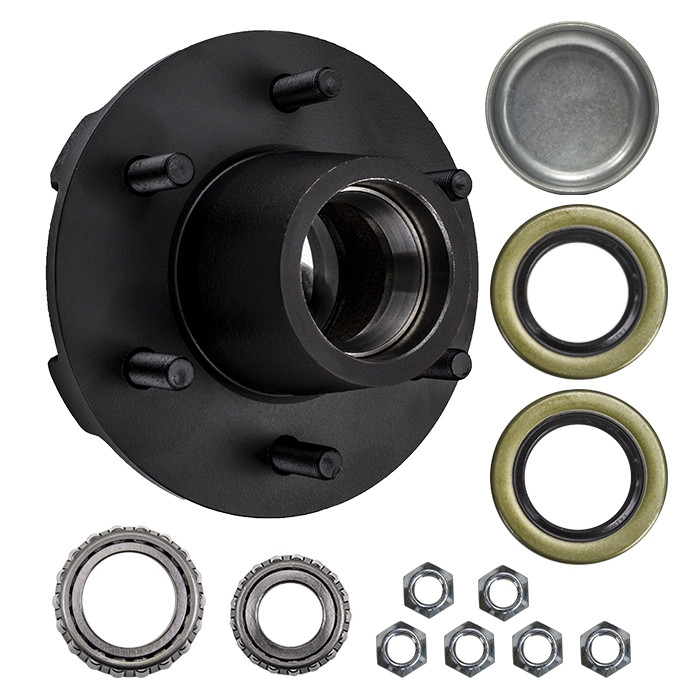
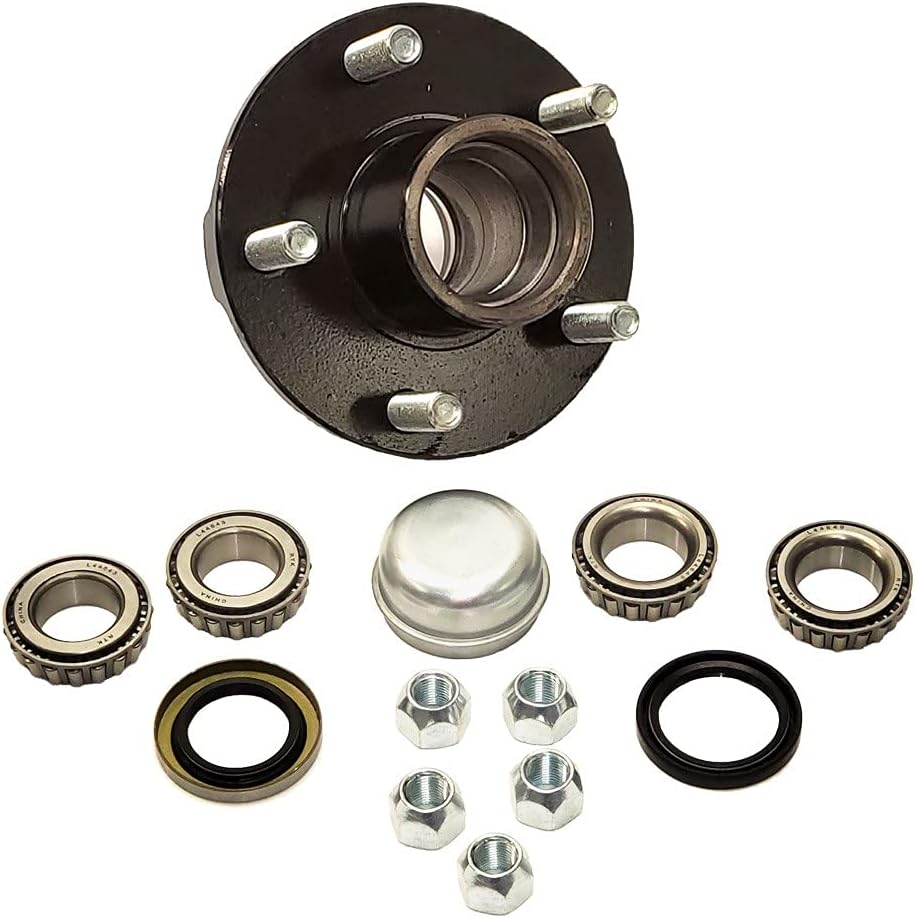
China Best Sales Front Axle Wheel Hub Bearing Wheel Hub Assembly 731679120 OE 1763887 for CZPT Transit bad axle symptoms
Product Description
Basic information for :
| Description | Wheel bearing repair kit 731679120 |
| Material | Chrome steel Gcr15 |
| Application | Ford Transit, Tourneo Custom Bus |
| Brand | SI, CZPT or customized |
| Size | OD: 208mm ID: 31mm FLANGE: 5 WEIGHT: 5kg WHEEL: 5-Hole |
| Packing | Neutral, SI, PPB brand packing or customized |
| OEM/ODM service | Yes |
| Manufacture place | ZHangZhoug, China |
| MOQ | 50 PCS |
| OEM replacement | Yes |
| Inspection | 100% |
| Warranty | 1 year or 30,000-50,000 KMS |
| Certificate | ISO9001:2015 |
| Payment | T/T, PayPal |
Detailed pictures:
OE No.:
For FORD: 1763887
For FORD: 1769170
For FORD: 2168129
For FORD: BK212C300AA
For FORD: BK212C300AB
For FORD: BK212C300AC
Other Ref. No.:
A.B.S. : 201860
AUTEX : 85717
Automotive Bearings : ABK2174
BENDIX : 052144B
F-AG :
FIRST LINE : FBK1469
FREMAX : FWB-1661
KAWE : 8530 16150
MOOG : FD-WB-12819
MOTAQUIP : LVBK1751
MOTAQUIP : LVBW1751
NK : 752547
OPTIMAL : 301905
TRISCAN : 8530 16150
AUTOKIT : 01.98286
AUTOKIT : ASB2881
AUTOKIT : RKB2881
REPKIT : RKB2881
Application:
FORD TOURNEO CUSTOM Bus 2.0 TDCi 2015-
FORD TOURNEO CUSTOM Bus 2.2 TDCi 2012-
FORD TRANSIT Box 2.2 TDCi 2013-
FORD TRANSIT Box 2.2 TDCi 4×4 2013-
Front Wheel Bearing Hub Assembly Replacement, Wheel Bearing & Hub Assembly, Hub Bearing Assembly, front bearing hub replacement, hub and bearing replacement, wheel hub bearings, front wheel bearing hub assembly, front wheel bearing hub replacement, hub bearing assembly front, wheel hub assembly, bearing assembly, Front Wheel Bearing and Hub Assembly, Front Wheel Drive Hub and Bearing Assembly
Packing and Delivery:
Work shop:
Exhibitions:
FAQ:
Q1.What is your shipping logistic?
Re: DHL, TNT, FedEx express, by air/sea/train.
Q2:What’s the MOQ?
Re: For the wheel hub assembly. The MOQ is always 50 sets. If ordering together with other models, small quantities can be organized. But need more time due to the production schedule.
Q3. What are your goods of packing?
Re: Generally, our goods will be packed in Neutral white or brown boxes for the hub bearing unit. Our brand packing SI & CZPT are offered. If you have any other packing requests, we shall also handle them.
Q4. What is your sample policy?
Re: We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock.
Q5. Do you have any certificates?
Re: Yes, we have the certificate of ISO9001:2015.
Q6:Any warranty of your products.
Re: Sure, We are offering a guarantee for 12 months or 40,000-50,000 km for the aftermarket.
Q7: How can I make an inquiry?
Re: You can contact us by email, telephone, WhatsApp, , etc.
Q8: How long can reply inquiry?
Re: Within 24 hours.
Q9: What’s the delivery time?
Re: Ready stock 10-15 days, production for 30 to 45 days.
Q10: How do you maintain our good business relationship?
Re: 1. Keep stable, reliable quality, competitive price to ensure our customer’s benefit;
2. Optimal lead time.
3. Keep customers updated about the new goods.
4. Make customers satisfaction as our main goal.
Q11: Can we visit the company & factory?
Re: Yes, welcome for your visit & business discussion.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Yes |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Yes |
| Type: | Wheel Hub Bearing |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Can you recommend reliable brands for purchasing replacement axle hubs?
When it comes to purchasing replacement axle hubs, there are several reliable brands known for their quality and durability. Here are some recommended brands:
- Timken: Timken is a well-known brand that specializes in manufacturing high-quality bearings and hub assemblies. They have a reputation for producing reliable and long-lasting products. Timken axle hubs are widely used in the automotive industry and are trusted by both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
- Moog: Moog is another reputable brand that offers a wide range of suspension and steering components, including axle hubs. Moog axle hubs are known for their precision engineering, excellent build quality, and reliable performance. They are designed to meet or exceed OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) specifications and are a popular choice among car owners.
- ACDelco: ACDelco is a trusted brand that provides a comprehensive range of automotive replacement parts. Their axle hubs are designed to deliver reliable performance and durability. ACDelco axle hubs are often recommended for their compatibility with various vehicle makes and models, making them a reliable choice for replacement.
- SKF: SKF is a well-established brand with a strong reputation in the automotive industry. They are known for their high-quality bearings and hub assemblies, including axle hubs. SKF axle hubs are engineered to provide excellent performance and longevity. They are often regarded as a premium option for those seeking reliable replacement parts.
- NTN: NTN is a trusted manufacturer of bearings and hub assemblies. They offer a range of axle hubs that are designed to meet stringent quality standards. NTN axle hubs are known for their durability and precise fitment, making them a reliable choice for replacement in various vehicles.
It’s important to note that the availability of specific brands may vary depending on your location and the make and model of your vehicle. Additionally, it’s always a good idea to consult with a trusted mechanic or do thorough research to ensure the compatibility of the axle hubs with your vehicle before making a purchase.
In summary, some reliable brands for purchasing replacement axle hubs include Timken, Moog, ACDelco, SKF, and NTN. These brands have a solid reputation for producing high-quality and durable axle hubs, making them trusted choices for maintaining and repairing your vehicle’s axle system.
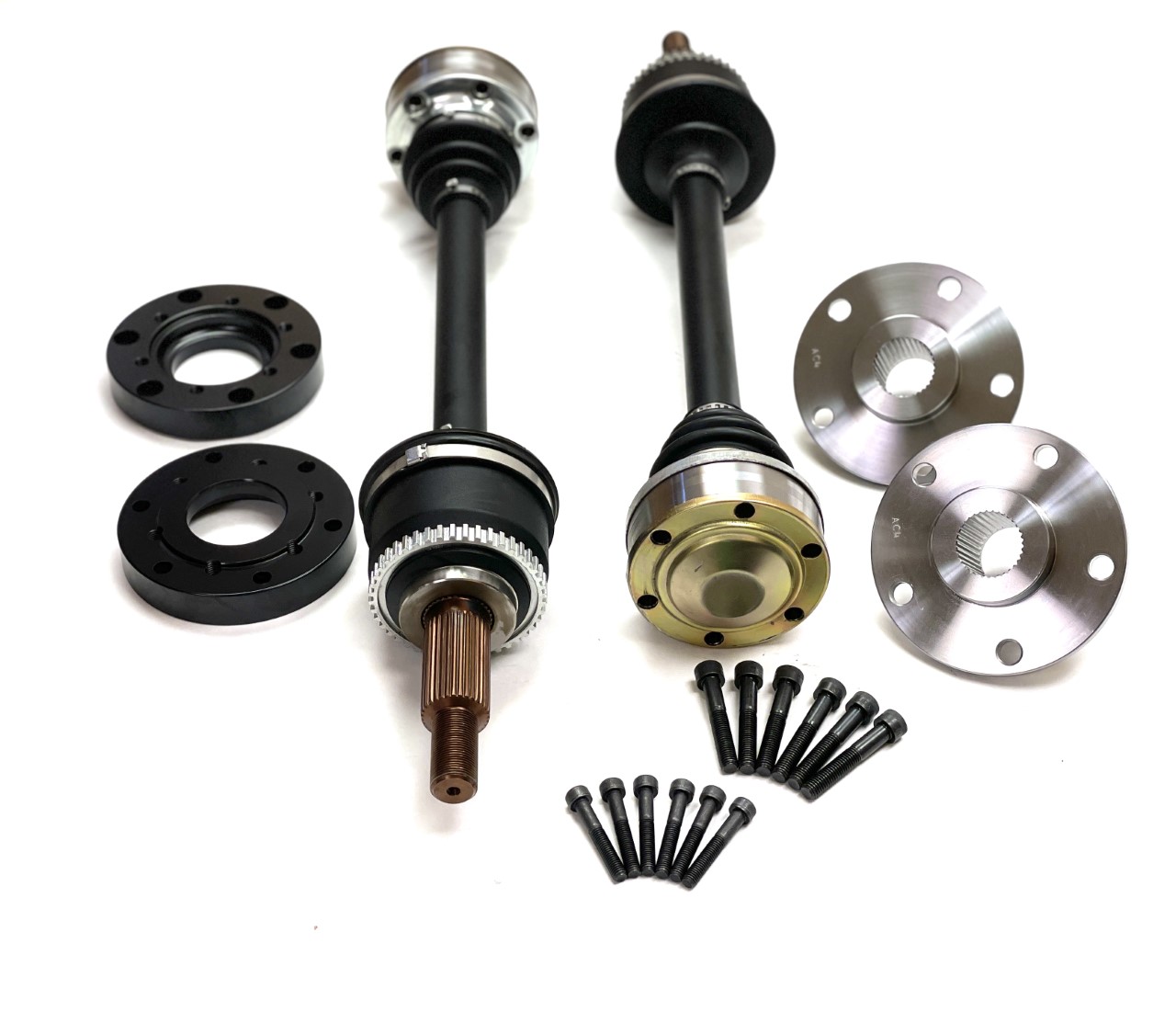

Can a worn or damaged wheel bearing impact the performance of an axle hub?
Yes, a worn or damaged wheel bearing can significantly impact the performance of an axle hub. The wheel bearing plays a crucial role in supporting the weight of the vehicle and allowing the wheels to rotate smoothly. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a worn or damaged wheel bearing can affect the performance of an axle hub:
- Wheel rotation: The axle hub, along with the wheel bearing, enables the smooth rotation of the wheel. When the wheel bearing is worn or damaged, it can cause irregular or uneven rotation of the wheel. This can result in vibrations, noise, and an overall rough ride quality.
- Excessive play: A worn wheel bearing may develop excessive play or looseness. This can cause the wheel to wobble or have noticeable movement when jacked up or when driving. Excessive play in the wheel bearing can affect the vehicle’s stability, handling, and control, making it more difficult to steer accurately.
- Noise: Worn or damaged wheel bearings often produce noticeable noise. The noise can vary from a low humming or rumbling sound to a high-pitched whining or grinding noise. The noise may become more pronounced when turning or when the vehicle is under load. Ignoring the noise and continuing to drive with a faulty wheel bearing can lead to further damage and potential safety hazards.
- Heat buildup: A damaged wheel bearing may generate excessive heat due to increased friction and inadequate lubrication. The heat buildup can cause the bearing to expand, leading to further damage and potential failure. Overheated wheel bearings can contribute to premature wear of other components within the axle hub assembly, such as the axle shaft or hub assembly itself.
- Uneven tire wear: A worn or damaged wheel bearing can result in uneven tire wear. As the wheel doesn’t rotate properly or experiences excessive play, it can cause the tire to wear unevenly. This can lead to premature tire wear on specific areas of the tread, affecting the tire’s performance, lifespan, and overall safety.
- Reduced fuel efficiency: When a wheel bearing is damaged or worn, it can create additional resistance and drag on the wheel. This increased rolling resistance can have a negative impact on fuel efficiency, causing the vehicle to consume more fuel to maintain speed and overcome the additional resistance. Thus, a faulty wheel bearing can lead to decreased fuel efficiency and increased operating costs.
It’s important to address any signs of a worn or damaged wheel bearing promptly. If you suspect a problem with the wheel bearing or experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is recommended to have the vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic or automotive technician. They can assess the condition of the wheel bearing and perform the necessary repairs or replacement to restore the proper performance of the axle hub and ensure safe operation of the vehicle.
In summary, a worn or damaged wheel bearing can have a significant impact on the performance of an axle hub. It can affect wheel rotation, cause excessive play, produce noise, lead to heat buildup, result in uneven tire wear, and reduce fuel efficiency. Prompt inspection and necessary repairs or replacement of a faulty wheel bearing are essential to maintain the optimal performance and safety of the axle hub.
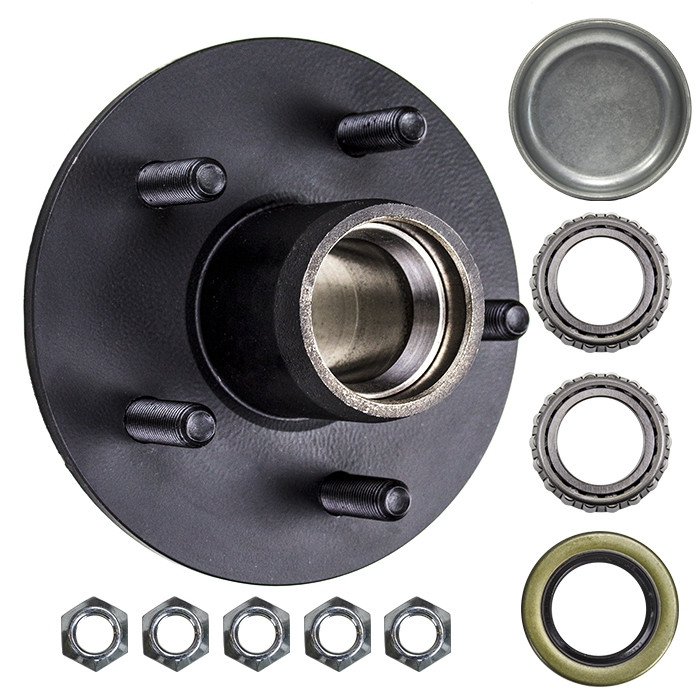

Are there any recalls or common issues associated with specific axle hub models?
Recalls and common issues can occur with specific axle hub models due to manufacturing defects, design flaws, or other factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
It’s important to note that specific recalls and common issues can vary depending on the make, model, and year of the vehicle, as well as the specific axle hub manufacturer. Manufacturers and regulatory bodies such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) monitor and address safety concerns related to axle hubs through recalls and investigations.
Recalls are typically initiated by the vehicle manufacturer or the axle hub manufacturer in response to identified safety defects or non-compliance with safety standards. Recalls aim to address the issues and rectify any potential safety risks associated with the axle hub models. They may involve inspections, repairs, or replacements of the affected components.
To determine if there are any recalls or common issues associated with specific axle hub models, it is recommended to check the following sources:
- Manufacturer’s Website: Visit the official website of the vehicle manufacturer or the axle hub manufacturer. They often provide information on recalls, technical service bulletins (TSBs), and common issues related to their products. Look for any relevant information specific to the axle hub models in question.
- NHTSA Website: The NHTSA maintains a comprehensive database of recalls and investigations related to vehicle components, including axle hubs. Their website allows users to search for recalls and investigations by specific make, model, and component. You can use their search tool to check if there are any recalls or investigations associated with the axle hub models of interest.
- Owner Forums and Online Communities: Online forums and communities dedicated to specific vehicle makes and models can be a valuable source of information. Owners often share their experiences, including common issues they have encountered with axle hub models. It’s important to consider multiple sources and exercise caution when relying on anecdotal information.
- Service Centers and Mechanics: Local service centers and mechanics who specialize in the specific vehicle make or have experience with the axle hub models in question may be aware of any recalls or common issues. They can provide insights based on their firsthand knowledge and experience.
By consulting these sources, you can gather information about any recalls or common issues associated with specific axle hub models. If any recalls or safety concerns are identified, it is recommended to contact the vehicle manufacturer or a certified dealership to inquire about the necessary actions, such as inspections or repairs, to address the issues.
In summary, recalls and common issues can occur with specific axle hub models. Checking the manufacturer’s website, the NHTSA website, owner forums, and consulting with service centers and mechanics can provide valuable information regarding any recalls or common issues associated with the axle hub models of interest. It’s important to stay informed and take appropriate actions to address any identified safety concerns.


editor by CX 2024-04-19
China Best Sales China Trailer Parts Classical Design Truck Trailer Parts Axle for Sell axle bearing
Product Description
Product Specification
| Axle Type | L4 | Wheer Fixing | Bearing | ||||||||||
| Max | L2 | L3 | GM Center | Studs | L1 | Rimis | Axle | ||||||
| Capacity | Track | Brake Size | Center | Axle Tube | Distance | D1 | D2 | Total | Recommended | Weight | |||
| (T) | (mm) | (mm) | Distance of | (mm) | of Brake | P.C.D. | Hole | Length | to use | (kg) | |||
| Spring Seat | Chamber | (mm) | Diameter | (mm) | |||||||||
| (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | |||||||||||
| CK12FB03G1DE | 12 | 1840 | ∈420×180 | ≥940 | 150x150x12 | 440 | 10-M22x1.5 | 335 | 281 | 2172 | 7.5V-20 | 380 | (Ouer)33213(lnner)33118 |
| CK13FB03G2DE | 13 | 1840 | ∈420×200 | ≥940 | 150x150x12 | 375 | 10-M22x1.5 | 335 | 281 | 2170 | 7.5V-20 | 381 | |
| CK14FB03G2FG | 14 | 1860 | ∈420×200 | ≥950 | 150x150x14 | 380 | 10-M22x1.5 | 335 | 281 | 2222 | 8.00V-20 | 412 | (Outer)33215 dnneri32219 |
| CK16FB0GG2HI | 16 | 1860 | ∈420×200 | ≥950 | 150x150x16 | 380 | 10-M22x1.5 | 335 | 281 | 2293 | 8.50V-20 | 439 | (Outer)32314(lnner)32222 |
| CK18FBC3GHI | 18 | 1860 | ∈420×220 | ≥950 | 150x150x18 | 380 | 10-M22x1.5 | 335 | 281 | 2293 | 8.50V-20 | 454 | (Outer)32314(lnner)32222 |
Product Display
Related Products
Packaging and Transportation
Customer Photo
Our Certificate
Company Profile
FAQ
FAQ:
1. Q:What’s your best price for this product?
A: We will quote you best price according to your quantity, so when you making an inquiry, please let us know the quantity you want.The more quantity the better price.
2. Q:How about the quality of this product?
A: Our products are certified to ISO9001, TS16949 international quality standards. We compay have very strict Quality Control Systems.
3. Q:What material of the product can you supply?
A: Steel
4. Q:What’s your MOQ?
A: 10pcs for each model. We hope you can buy more to save more money.
5. Q:What’s the delivery time?
A: For products that are in stock, we can ship it within 7 days after receiving your payment. For custom order, quantity within 24 tons, production time is 12-20 days after confirmed every details.
6. Q:What’s your packing?
A:Our usual packing for this product is pallet, we can also supply you packing according to your requirements.
7. Q:Can we custom our own logo or label on this product?
A: Yes, you can. we support logo print & stamping & label print, print will be free if the logo is not very complex.
8. Q:What about the warranty?
A: We are very confident in our products, and we pack them very well to make sure the goods in well protection.
To avoid any subsequent trouble regarding quality issue, we suggest that you check the springs once you receive them. If there is any transport damaged or quality issue, don’t forget take the detail pictrues and contact us as soon as possible,we will properly handle it, make sure your loss to reduce to the smallest .
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | After Sales Service |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Application: | Trailer |
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
| Material: | Steel |
| Type: | Front Axles |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
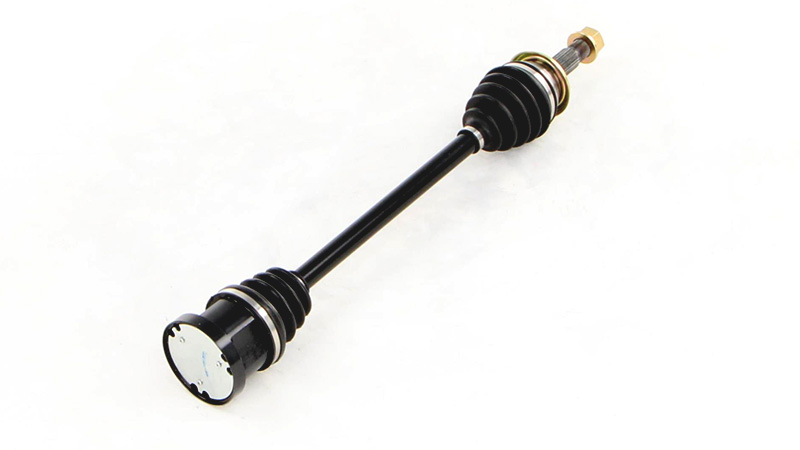

Can you provide insights into the maintenance of axle bearings for smooth operation?
Maintaining axle bearings is essential for ensuring smooth operation, longevity, and optimal performance of a vehicle’s axle system. Here are some insights into the maintenance of axle bearings:
1. Regular Inspection:
Perform regular visual inspections of the axle bearings to check for any signs of wear, damage, or leaks. Look for indications such as excessive play, unusual noises, vibration, or leakage of grease. Inspections should be carried out as per the manufacturer’s recommended intervals or during routine maintenance checks.
2. Lubrication:
Adequate lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation of axle bearings. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the type of lubricant to use and the recommended intervals for greasing. Over-greasing or under-greasing can lead to bearing damage or failure. Ensure that the proper amount of grease is applied to the bearings, and use a high-quality grease that is compatible with the axle bearing specifications.
3. Seal Inspection and Replacement:
Check the condition of the axle bearing seals regularly. The seals help to keep contaminants out and retain the lubricating grease within the bearing. If the seals are damaged, worn, or show signs of leakage, they should be replaced promptly to prevent dirt, water, or debris from entering the bearing assembly and causing damage.
4. Proper Installation:
During axle bearing replacement or installation, it is crucial to follow proper procedures to ensure correct seating and alignment. Improper installation can lead to premature bearing failure and other issues. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or consult a professional mechanic to ensure proper installation techniques are followed.
5. Load Capacity and Alignment:
Ensure that the axle bearings are properly sized and rated to handle the load capacity of the vehicle and the specific application. Overloading the bearings can lead to excessive wear and premature failure. Additionally, proper wheel alignment is important to prevent uneven bearing wear. Regularly check and adjust the wheel alignment if necessary.
6. Environmental Considerations:
Take into account the operating conditions and environment in which the vehicle is used. Extreme temperatures, exposure to water, dirt, or corrosive substances can affect the performance of axle bearings. In such cases, additional preventive measures may be necessary, such as more frequent inspections, cleaning, and lubrication.
7. Professional Maintenance:
If you are unsure about performing maintenance on axle bearings yourself or if you encounter complex issues, it is recommended to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or technician who has experience with axle systems. They can provide expert advice, perform necessary repairs or replacements, and ensure proper maintenance of the axle bearings.
By following these maintenance insights, you can help ensure the smooth operation, longevity, and reliability of axle bearings, contributing to the overall performance and safety of the vehicle.
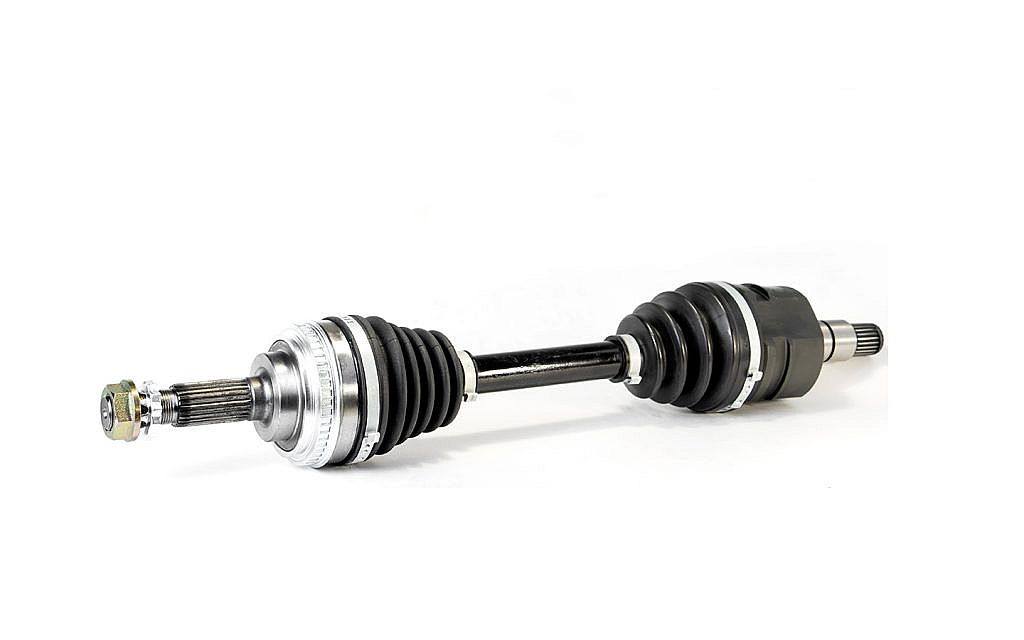

Can you recommend axle manufacturers known for durability and reliability?
When it comes to choosing axle manufacturers known for durability and reliability, there are several reputable companies in the automotive industry. While individual experiences and preferences may vary, the following axle manufacturers have a track record of producing high-quality products:
1. Dana Holding Corporation: Dana is a well-known manufacturer of axles, drivetrain components, and sealing solutions. They supply axles to various automotive manufacturers and have a reputation for producing durable and reliable products. Dana axles are commonly found in trucks, SUVs, and off-road vehicles.
2. AAM (American Axle & Manufacturing): AAM is a leading manufacturer of driveline and drivetrain components, including axles. They supply axles to both OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) and the aftermarket. AAM axles are known for their durability and are often found in trucks, SUVs, and performance vehicles.
3. GKN Automotive: GKN Automotive is a global supplier of driveline systems, including axles. They have a strong reputation for producing high-quality and reliable axles for a wide range of vehicles. GKN Automotive supplies axles to various automakers and is recognized for their technological advancements in the field.
4. Meritor: Meritor is a manufacturer of axles, brakes, and other drivetrain components for commercial vehicles. They are known for their robust and reliable axle products that cater to heavy-duty applications in the commercial trucking industry.
5. Spicer (Dana Spicer): Spicer, a division of Dana Holding Corporation, specializes in manufacturing drivetrain components, including axles. Spicer axles are widely used in off-road vehicles, trucks, and SUVs. They are known for their durability and ability to withstand demanding off-road conditions.
6. Timken: Timken is a trusted manufacturer of bearings, seals, and other mechanical power transmission products. While they are primarily known for their bearings, they also produce high-quality axle components used in various applications, including automotive axles.
It’s important to note that the availability of specific axle manufacturers may vary depending on the region and the specific vehicle make and model. Additionally, different vehicles may come equipped with axles from different manufacturers as per the OEM’s selection and sourcing decisions.
When considering axle replacements or upgrades, it is advisable to consult with automotive experts, including mechanics or dealerships familiar with your vehicle, to ensure compatibility and make informed decisions based on your specific needs and requirements.

What are the signs of a worn or failing axle, and how can I troubleshoot axle issues?
Identifying the signs of a worn or failing axle is important for maintaining the safety and functionality of your vehicle. Here are some common signs to look out for and troubleshooting steps you can take to diagnose potential axle issues:
- Unusual Noises:
- Vibrations:
- Uneven Tire Wear:
- Difficulty Steering:
- Visible Damage or Leaks:
- Professional Inspection:
If you hear clunking, clicking, or grinding noises coming from the area around the wheels, it could indicate a problem with the axle. These noises may occur during acceleration, deceleration, or when turning. Troubleshoot by listening carefully to the location and timing of the noises to help pinpoint the affected axle.
A worn or failing axle can cause vibrations that can be felt through the steering wheel, floorboard, or seat. These vibrations may occur at certain speeds or during specific driving conditions. If you experience unusual vibrations, it’s important to investigate the cause, as it could be related to axle problems.
Inspect your tires for uneven wear patterns. Excessive wear on the inner or outer edges of the tires can be an indication of axle issues. Misaligned or damaged axles can cause the tires to tilt, leading to uneven tire wear. Regularly check your tires for signs of wear and take note of any abnormalities.
A worn or damaged axle can affect steering performance. If you experience difficulty in steering, such as stiffness, looseness, or a feeling of the vehicle pulling to one side, it may be due to axle problems. Pay attention to any changes in steering responsiveness and address them promptly.
Inspect the axles visually for any signs of damage or leaks. Look for cracks, bends, or visible fluid leaks around the axle boots or seals. Damaged or leaking axles can lead to lubrication loss and accelerated wear. If you notice any visible issues, it’s important to have them inspected and repaired by a qualified mechanic.
If you suspect axle issues but are unsure about the exact cause, it’s advisable to seek a professional inspection. A qualified mechanic can perform a thorough examination of the axles, suspension components, and related systems. They have the expertise and tools to diagnose axle problems accurately and recommend the appropriate repairs.
It’s important to note that troubleshooting axle issues can sometimes be challenging, as symptoms may overlap with other mechanical problems. If you’re uncertain about diagnosing or repairing axle issues on your own, it’s recommended to consult a professional mechanic. They can provide a proper diagnosis, ensure the correct repairs are performed, and help maintain the safety and performance of your vehicle.


editor by CX 2024-02-20
China factory CZPT Brand Hot Sales Automotive Bearing Front Axle Wheel Hub for CZPT Explorer 515050 Wheel Assembly Car Spare Part axle bearing
Product Description
Company Profile
Company introduction:
This is from GUANXIAN HAGUAN BEARING CO.,LTD.,located in China.WHB is our brand. We specialize in manufacturing double-row spherical roller bearing,pillow block bearing,thrust ball bearing and so on . We could supply bearing for you with competitive price or best price. Our products are sold well to Russia, Brazil, Mexico, Poland and Tunisia ect. If you are interested in our products, please send the enquiry to us as soon as possible. If you have any questions about the bearing can consult me.
Hope to establish a good business relationship with you. Looking forward to your early reply.
Thanks and best regards.
Certifications
ISO Certificate:
CE Certificate:
Packaging & Shipping
Detailed Photos
Packing:
A. plastic box+outer carton+pallets
B. plastic bag+ single box+carton+pallet
C. plastic bag+ single box+middle box+carton+pallet
D. Of course we will also be based on your needs
FAQ
FAQ:
1. What’s the minimum order quantity of your company?
our minimum order is one.
2. Can you accept OEM and customize it?
Yes, we can customize it for you according to the samples or drawings.
3. Can you provide samples for free?
Yes, we can provide samples free of charge, but we need our customers to bear the freight.
4.Is your company a factory or a trading company?
we have our own factories. We export bearings all over the world.
5. When is the warranty period of your bearings?
within 3 months, the customer needs to provide photos and return the bearing.
6.Can you tell me your company’s payment terms are acceptable?
T / T, D / P, L / C, Western Union remittance,Paypal,Money Gram….
7.Can you tell me the delivery time of your goods?
7-15 days, mainly depending on the quantity of your order.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Contact Angle: | 60° |
|---|---|
| Aligning: | Non-Aligning Bearing |
| Separated: | Separated |
| Rows Number: | Single |
| Material: | Bearing Steel |
| ISO: | 9001 |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.5/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do I diagnose and address noise issues associated with a malfunctioning axle hub?
Diagnosing and addressing noise issues associated with a malfunctioning axle hub requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause and take appropriate corrective measures. Here’s a detailed explanation of the diagnostic process and steps to address the problem:
1. Identify the Noise:
The first step is to identify the specific noise associated with the malfunctioning axle hub. Pay attention to the type and characteristics of the noise, such as grinding, growling, clicking, or humming. Note when the noise occurs, whether it’s during acceleration, deceleration, or while turning. This initial identification can help narrow down the possible causes.
2. Inspect the Axle Hub:
Visually inspect the axle hub for any signs of damage or wear. Look for cracks, corrosion, or loose components. Check if there is any leaking grease around the hub, as it can indicate bearing failure. A thorough inspection can provide valuable clues about the condition of the axle hub.
3. Perform a Road Test:
Take the vehicle for a road test to observe the noise and its behavior under different driving conditions. Pay attention to any changes in the noise when making turns, accelerating, or braking. Note whether the noise gets louder or changes in pitch. This can help in further narrowing down the issue.
4. Jack up the Vehicle:
If the noise persists and is suspected to be coming from the axle hub, jack up the vehicle and secure it with jack stands. Rotate the wheel associated with the suspected axle hub and listen for any abnormal noise or roughness. Try to wiggle the wheel by hand to check for excessive play or looseness, which can indicate a problem with the hub assembly.
5. Check Wheel Bearings:
A common cause of noise issues in axle hubs is worn-out or damaged wheel bearings. To check the wheel bearings, grasp the tire at the 12 o’clock and 6 o’clock positions and attempt to rock it back and forth. Excessive movement or play indicates a potential problem with the wheel bearings. Additionally, spin the wheel and listen for any grinding or rumbling noises, which can also be indicative of bearing issues.
6. Addressing the Issue:
If a malfunctioning axle hub is identified as the source of the noise, the following steps can be taken to address the problem:
- Replacement: If the axle hub is severely damaged or the bearings are worn out, replacing the entire hub assembly is often recommended. This ensures proper fitment, bearing integrity, and overall reliability. Consult the vehicle’s service manual or seek professional assistance for the correct replacement procedure.
- Bearing Replacement: In some cases, it may be possible to replace the wheel bearings within the axle hub if they are the sole source of the noise issue. This requires specialized tools and expertise, so it is advisable to consult a qualified mechanic for bearing replacement.
- Additional Repairs: Depending on the severity of the issue, it may be necessary to address other related components. This can include replacing damaged CV joints, inspecting and replacing worn brake components, or addressing any other issues identified during the diagnostic process.
7. Post-Repair Verification:
After addressing the noise issue by repairing or replacing the malfunctioning axle hub, take the vehicle for a test drive to verify that the noise is eliminated. Ensure that the vehicle operates smoothly, and there are no abnormal vibrations or noises coming from the axle hub during different driving conditions.
It’s important to note that diagnosing and addressing noise issues associated with a malfunctioning axle hub can be complex, and it may require the expertise of a qualified mechanic. If you’re uncomfortable performing the diagnostics and repairs yourself, it’s advisable to seek professional assistance to ensure an accurate diagnosis and proper resolution of the issue.
In summary, diagnosing and addressing noise issues associated with a malfunctioning axle hub involves identifying the noise, inspecting the hub, performing a road test, checking wheel bearings, and taking appropriate repair or replacement measures. Following a systematic approach and seeking professional help when needed can help resolve the noise issue and ensure the safe operation of the vehicle.

Are there specific tools required for DIY axle hub replacement, and where can I find them?
When undertaking a DIY axle hub replacement, certain tools are needed to ensure a smooth and successful process. Here are some specific tools that are commonly required for DIY axle hub replacement and where you can find them:
- Jack and jack stands: These tools are essential for raising the vehicle off the ground and providing a stable support system. You can find jacks and jack stands at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Lug wrench or socket set: A lug wrench or a socket set with the appropriate size socket is necessary to loosen and tighten the lug nuts on the wheel. These tools are commonly available at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Torque wrench: A torque wrench is required to tighten the lug nuts on the wheel and other fasteners to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications. Torque wrenches can be found at automotive supply stores, tool stores, and online retailers.
- Pry bar: A pry bar is useful for gently separating the axle hub assembly from the mounting point, especially if it is tightly secured. Pry bars are available at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Hammer: A hammer can be used to tap or lightly strike the axle hub assembly or its components for removal or installation. Hammers are commonly available at hardware stores, tool stores, and online retailers.
- Wheel bearing grease: High-quality wheel bearing grease is necessary for lubricating the axle hub assembly and ensuring smooth operation. Wheel bearing grease can be purchased at automotive supply stores, lubricant suppliers, and online retailers.
- Additional tools: Depending on the specific vehicle and axle hub assembly, you may require additional tools such as a socket set, wrenches, pliers, or specific specialty tools. Consult the vehicle’s service manual or online resources for the specific tools needed for your vehicle model.
To find these tools, you can visit local automotive supply stores, hardware stores, or tool stores in your area. They typically carry a wide range of automotive tools and equipment. Alternatively, you can explore online retailers that specialize in automotive tools and equipment, where you can conveniently browse and purchase the tools you need.
It’s important to ensure that the tools you acquire are of good quality and suitable for the task at hand. Investing in quality tools can make the DIY axle hub replacement process more efficient and help achieve better results. Additionally, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines when using tools and equipment.
In summary, specific tools are required for DIY axle hub replacement, such as a jack and jack stands, lug wrench or socket set, torque wrench, pry bar, hammer, and wheel bearing grease. These tools can be found at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, tool stores, and online retailers. Acquiring quality tools and following proper safety guidelines will contribute to a successful DIY axle hub replacement.

How do changes in wheel offset affect the angles and performance of axle hubs?
Changes in wheel offset can have a significant impact on the angles and performance of axle hubs. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Wheel offset refers to the distance between the centerline of the wheel and the mounting surface. It determines how far the wheel and tire assembly will be positioned in relation to the axle hub. There are three types of wheel offsets: positive offset, zero offset, and negative offset.
Here’s how changes in wheel offset can affect the angles and performance of axle hubs:
- Camber Angle: Camber angle refers to the inward or outward tilt of the wheel when viewed from the front of the vehicle. Changes in wheel offset can impact the camber angle. Increasing positive offset or reducing negative offset typically results in more positive camber, while increasing negative offset or reducing positive offset leads to more negative camber. Improper camber angle can cause uneven tire wear, reduced traction, and handling issues.
- Track Width: Wheel offset affects the track width, which is the distance between the centerlines of the left and right wheels. Wider track width can improve stability and cornering performance. Increasing positive offset or reducing negative offset generally widens the track width, while increasing negative offset or reducing positive offset narrows it.
- Steering Geometry: Changes in wheel offset also impact the steering geometry of the vehicle. Altering the offset can affect the scrub radius, which is the distance between the tire contact patch and the steering axis. Changes in scrub radius can influence steering effort, feedback, and stability. It’s important to maintain the appropriate scrub radius for optimal handling and performance.
- Wheel Bearing Load: Wheel offset affects the load applied to the wheel bearings. Increasing positive offset or reducing negative offset generally increases the load on the inner wheel bearing, while increasing negative offset or reducing positive offset increases the load on the outer wheel bearing. Proper wheel bearing load is crucial for their longevity and performance.
- Clearance and Interference: Changes in wheel offset can also impact the clearance between the wheel and suspension components or bodywork. Insufficient clearance due to excessive positive offset or inadequate clearance due to excessive negative offset can lead to rubbing, interference, or potential damage to the axle hub, suspension parts, or bodywork.
It’s important to note that any changes in wheel offset should be done within the manufacturer’s recommended specifications or in consultation with knowledgeable professionals. Deviating from the recommended wheel offset can lead to adverse effects on the axle hub angles and performance, as well as other aspects of the vehicle’s handling and safety.
When modifying wheel offset, it is crucial to consider the overall impact on the vehicle’s suspension geometry, clearance, and alignment. It may be necessary to make corresponding adjustments to maintain proper alignment angles, such as camber, toe, and caster, to ensure optimal tire wear, handling, and performance.
In summary, changes in wheel offset can have a significant impact on the angles and performance of axle hubs. They can affect camber angles, track width, steering geometry, wheel bearing load, and clearance. It is important to adhere to manufacturer’s specifications and consult with knowledgeable professionals when considering changes in wheel offset to ensure proper alignment, optimal performance, and safe operation of the vehicle.


editor by CX 2024-02-20
China Best Sales OEM BMW Parts Replacement 31206850158 713649510 R150.47 Front Axle Wheel Bearing and Hub Assemblies Kit axle barbell
Product Description
Quick view:
| Name | FRONT AXLE WHEEL BEARING KIT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material | steel GCr15, 65Mn, or 55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Application | BMW ROLLS-ROYCE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bolts | 4 bolts | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight | 3.8kg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brand | SI, PPB, or customized | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Packing | According to the customer, Neutral, our brand packing or customized | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OEM replacement | Yes, design according to the BMW genuine parts | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacture place | ZHangZhoug, China | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOQ | 20 PCS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warranty | 1 year or 30, BMW : 31206791 BMW : BMW : Ref.: Application: How we are controlling our quality of the automotive bearing: FAQ: Q: How about your delivery time?
Q: What is your sample policy? Q: How can I make an inquiry? Q: How long can reply inquiry?
What steps are involved in the proper removal and installation of an axle hub assembly?Properly removing and installing an axle hub assembly requires a systematic approach and the use of appropriate tools. Here are the detailed steps involved in the process:
It’s important to note that the specific steps and procedures may vary depending on the vehicle make and model. Always consult the vehicle’s service manual or seek professional assistance if you are unsure about any aspect of the removal and installation process. In summary, the proper removal and installation of an axle hub assembly involve gathering the necessary tools, preparing the vehicle, jacking up the vehicle, removing the wheel, disconnecting brake components and the axle, removing the old axle hub assembly, cleaning and inspecting, installing the new assembly, reconnecting brake components, reinstalling the wheel, and finally testing and verifying the functionality of the axle hub assembly.
How often should axle hubs be inspected and replaced as part of routine vehicle maintenance?Regular inspection and maintenance of axle hubs are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a vehicle. The frequency of inspection and replacement may vary depending on several factors, including the vehicle’s make and model, driving conditions, and manufacturer’s recommendations. Here are some guidelines to consider:
It’s important to note that the intervals for inspecting and replacing axle hubs can vary significantly between different vehicles. Therefore, it is recommended to consult the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations to determine the specific maintenance schedule for your vehicle. Additionally, if you are unsure or suspect any issues with the axle hubs, it is advisable to have a qualified mechanic or automotive technician inspect and assess the condition of the axle hubs. In summary, the frequency of inspecting and replacing axle hubs as part of routine vehicle maintenance depends on factors such as the manufacturer’s recommendations, driving conditions, visual inspections, wheel bearing maintenance requirements, and the presence of any unusual noises or vibrations. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and promptly addressing any abnormalities will help ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the axle hubs.
Can axle hubs be upgraded for better performance, and if so, how?Axle hubs can be upgraded to improve performance in certain cases. Upgrading axle hubs can involve various modifications and enhancements. Here’s a detailed explanation: Before considering an upgrade, it’s important to evaluate the specific needs and goals for the vehicle. Upgrades to axle hubs can target areas such as durability, load capacity, handling, and overall performance. Here are some potential ways to upgrade axle hubs:
It’s important to note that axle hub upgrades may require careful consideration of compatibility with other vehicle components, such as brakes, wheels, and suspension. Additionally, some upgrades may affect the vehicle’s warranty or require professional installation. It is recommended to consult with knowledgeable professionals, such as mechanics or specialists, who can provide guidance on suitable upgrades and ensure proper installation. When considering axle hub upgrades, it’s also essential to assess the overall condition of the vehicle and address any underlying issues. Regular maintenance, such as proper lubrication, inspection, and timely replacement of worn components, is crucial for maximizing the performance and lifespan of the axle hubs. In summary, axle hubs can be upgraded to improve performance in certain cases. Upgrades may involve high-performance bearings, improved seals, reinforced hub components, enhanced cooling, performance coatings, or aftermarket axle hub assemblies. It’s important to assess the specific needs of the vehicle, consult with professionals, and consider compatibility with other components when pursuing axle hub upgrades.
China Best Sales Front Axle Wheel Hub Assembly Vkba3511 for Opel Astra Vauxhall Astra 13123486 1603209 90538940 9117620 Wheel Hub Bearing Unit axle costProduct Description
Product Description
Detailed Photos Front Axle Wheel Hub Assembly Vkba3511 for Opel Astra Vauxhall Astra 13123486~8 9117620 Wheel Hub Bearing Unit OEM NUMBER
REFERENCE NUMBER
Company Profile
ZheJiang Mighty Machinery Co. Ltd is a professional manufacturer of auto bearings for more than 20 years. We provide a one-stop service for our customers. Our main products include wheel bearings & hub assembly, belt tensioners, clutch release bearings, and other parts. Relying on the professional and rich manufacturing experience and many substantial factories which stable cooperated for many years, Mighty suppliers customers high-quality products at very competitive prices.
Customer satisfaction is our First Priority, We adhere to the concept of ” Quality First, Customer First”. We will continue to provide high-quality products and the best services to our customers and build up CZPT long-time friendship partners.
Our Advantages More than 20 years of manufacturing and exporting experience Packaging & Shipping FAQ 1. What’s the minimum order quantity? We don’t have the minimum order quantity. We can also provide free samples, but you need to pay the freight. Yes, we provide ODM&OEM services to customers around the world, and we can customize different brands and different sizes of packaging boxes according to customers’ requirements. We guarantee that our products will be free from defects in materials and workmanship within 12 months from the date of delivery. The warranty is void due to improper use, incorrect installation, and physical damage. 4. How to place an order? Send us an email with the models, brand, quantity, consignee information, model of transportation, and payment 5. What are your packing conditions? We use standardized export packaging and environmental protection packaging materials. If you have a legally registered patent, we will package the goods in your brand box after receiving your authorization 6. What are your payment terms? T/T is 30% of the payment in advance and 70% balance before delivery. Before you pay the balance, we will show you photos or videos of the products and packaging. 7. How long is your delivery time? The delivery time of a sample order is 3-5 days, and that of a batch order is 5-45 days. The exact delivery time depends on the item and the quantity you ordered. 8. Do you test all products before delivery? /* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
What are the common symptoms of a failing axle hub, and how can they be identified?Identifying the common symptoms of a failing axle hub is crucial for timely diagnosis and repair. Here’s a detailed explanation of the common symptoms and how they can be identified: 1. Wheel Vibrations: One of the common symptoms of a failing axle hub is noticeable wheel vibrations. As the hub becomes worn or damaged, it may cause the wheel to wobble or shake while driving. These vibrations can be felt through the steering wheel, floorboard, or seat. To identify this symptom, pay attention to any unusual vibrations that occur, especially at higher speeds. 2. Grinding or Growling Noises: A failing axle hub can produce grinding or growling noises. This can be an indication of worn-out or damaged wheel bearings within the hub. The noise may vary in intensity, and it is often more pronounced during turns or when the vehicle is in motion. To identify this symptom, listen for any unusual grinding or growling sounds coming from the wheels while driving. 3. Wheel Play or Looseness: A failing axle hub can result in wheel play or looseness. When the hub is damaged or worn, it may not provide a secure mounting point for the wheel. As a result, the wheel may have excessive play or feel loose when you attempt to wiggle it by hand. To identify this symptom, jack up the vehicle and try to move the wheel in different directions to check for any abnormal movement. 4. Uneven Tire Wear: A failing axle hub can contribute to uneven tire wear. If the hub is damaged, it can affect the alignment and cause the tire to wear unevenly. Look for signs of abnormal tire wear, such as excessive wear on one side of the tire or feathering patterns. Uneven tire wear may also be accompanied by other symptoms, such as vibrations or pulling to one side while driving. 5. ABS Warning Light: In some cases, a failing axle hub can trigger the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) warning light on the vehicle’s dashboard. This can occur if there is a problem with the wheel speed sensor, which is often integrated into the hub assembly. The ABS warning light indicates a fault in the braking system and should be diagnosed using a diagnostic tool by a qualified technician. 6. Visual Inspection: A visual inspection can also help identify signs of a failing axle hub. Look for any visible damage or wear on the hub, such as cracks, corrosion, or bent flanges. Additionally, check for any leaking grease around the hub or signs of excessive heat, which can indicate bearing failure. 7. Professional Diagnosis: If you suspect a failing axle hub but are unsure, it is recommended to have the vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic. They can perform a comprehensive examination of the wheel assembly, including the hub, bearings, and associated components. They may use specialized tools and equipment to measure wheel play, check for bearing wear, and assess the overall condition of the hub. In summary, common symptoms of a failing axle hub include wheel vibrations, grinding or growling noises, wheel play or looseness, uneven tire wear, ABS warning light activation, and visible damage. It is essential to pay attention to these symptoms and seek professional diagnosis and repair to prevent further damage and ensure the safe operation of the vehicle.
Are there aftermarket axle hubs available with enhanced durability or performance features?Yes, there are aftermarket axle hubs available with enhanced durability or performance features. Aftermarket parts are components that are produced by manufacturers other than the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) of the vehicle. These aftermarket axle hubs are designed to provide improved durability, performance, or other specialized features compared to the stock OEM axle hubs. Here’s a detailed explanation:
It’s worth noting that while aftermarket axle hubs can offer enhanced durability or performance features, not all aftermarket parts are created equal. The quality and performance of aftermarket axle hubs can vary depending on the manufacturer and brand. It’s advisable to choose reputable aftermarket brands that have a track record of producing reliable and high-quality components. Consulting with automotive professionals or enthusiasts and reading customer reviews can also provide valuable insights when selecting aftermarket axle hubs. In summary, aftermarket axle hubs with enhanced durability or performance features are available. These aftermarket options may incorporate design improvements, specialized materials, or performance-oriented features to offer increased durability, improved performance, or compatibility with specialized applications. Conducting thorough research and selecting reputable aftermarket brands can help ensure the quality and compatibility of the aftermarket axle hubs for your vehicle.
How do changes in wheel offset affect the angles and performance of axle hubs?Changes in wheel offset can have a significant impact on the angles and performance of axle hubs. Here’s a detailed explanation: Wheel offset refers to the distance between the centerline of the wheel and the mounting surface. It determines how far the wheel and tire assembly will be positioned in relation to the axle hub. There are three types of wheel offsets: positive offset, zero offset, and negative offset. Here’s how changes in wheel offset can affect the angles and performance of axle hubs:
It’s important to note that any changes in wheel offset should be done within the manufacturer’s recommended specifications or in consultation with knowledgeable professionals. Deviating from the recommended wheel offset can lead to adverse effects on the axle hub angles and performance, as well as other aspects of the vehicle’s handling and safety. When modifying wheel offset, it is crucial to consider the overall impact on the vehicle’s suspension geometry, clearance, and alignment. It may be necessary to make corresponding adjustments to maintain proper alignment angles, such as camber, toe, and caster, to ensure optimal tire wear, handling, and performance. In summary, changes in wheel offset can have a significant impact on the angles and performance of axle hubs. They can affect camber angles, track width, steering geometry, wheel bearing load, and clearance. It is important to adhere to manufacturer’s specifications and consult with knowledgeable professionals when considering changes in wheel offset to ensure proper alignment, optimal performance, and safe operation of the vehicle.
China Good quality Trailer Parts 5X4.5″ Trailer Hubs Trailer Idler Hub Non-Brake Wheel Hub Kit with Bearing and Spindle with Best Sales
Product Description
Product Description
Product Parameters
Packaging & Shipping
Our Advantages
Company Profile HangZhou Tsingleader Industry Co., Ltd. is located in the beautiful HangZhou city. We specialize in the production of trailer parts, axle and transmission of engineering machinery and special engineering and agricultural machinery.
Screw Sizes and Their UsesScrews have different sizes and features. This article will discuss screw sizes and their uses. There are 2 main types: right-handed and left-handed screw shafts. Each screw features a point that drills into the object. Flat tipped screws, on the other hand, need a pre-drilled hole. These screw sizes are determined by the major and minor diameters. To determine which size of screw you need, measure the diameter of the hole and the screw bolt’s thread depth. The major diameter of a screw shaftThe major diameter of a screw shaft is the distance from the outer edge of the thread on 1 side to the tip of the other. The minor diameter is the inner smooth part of the screw shaft. The major diameter of a screw is typically between 2 and 16 inches. A screw with a pointy tip has a smaller major diameter than 1 without. In addition, a screw with a larger major diameter will have a wider head and drive. The pitch diameter of a screw shaftWhen choosing the appropriate screw, it is important to know its pitch diameter and pitch line. The pitch line designates the distance between adjacent thread sides. The pitch diameter is also known as the mean area of the screw shaft. Both of these dimensions are important when choosing the correct screw. A screw with a pitch of 1/8 will have a mechanical advantage of 6.3. For more information, consult an application engineer at Roton. The thread depth of a screw shaftOften referred to as the major diameter, the thread depth is the outermost diameter of the screw. To measure the thread depth of a screw, use a steel rule, micrometer, or caliper. In general, the first number in the thread designation indicates the major diameter of the thread. If a section of the screw is worn, the thread depth will be smaller, and vice versa. Therefore, it is good practice to measure the section of the screw that receives the least amount of use. The lead of a screw shaftPitch and lead are 2 measurements of a screw’s linear distance per turn. They’re often used interchangeably, but their definitions are not the same. The difference between them lies in the axial distance between adjacent threads. For single-start screws, the pitch is equal to the lead, while the lead of a multi-start screw is greater than the pitch. This difference is often referred to as backlash. The thread angle of a screw shaftThe angle between the axes of a thread and the helix of a thread is called the thread angle. A unified thread has a 60-degree angle in all directions. Screws can have either a tapped hole or a captive screw. The screw pitch is measured in millimeters (mm) and is usually equal to the screw major diameter. In most cases, the thread angle will be equal to 60-degrees. The tapped hole (or nut) into which the screw fitsA screw can be re-threaded without having to replace it altogether. The process is different than that of a standard bolt, because it requires threading and tapping. The size of a screw is typically specified by its major and minor diameters, which is the inside distance between threads. The thread pitch, which is the distance between each thread, is also specified. Thread pitch is often expressed in threads per inch.
China Standard Rear Left Wheel Hub Bearing for CZPT Lexus OE 42460-60010 42460-60020 42410-60060 2dacf044n-4L 512227 Ha594246 Grw271 9244004 Wheel Hub Unit with Best Sales
Product Description
Product Description
Company Profile
ZheJiang Mighty Machinery Co. Ltd is a professional manufacturer of auto bearings for more than 20 years. We provide a one-stop service for our customers. Our main products include wheel bearings & hub assembly, belt tensioners, clutch release bearings, and other parts. Relying on the professional and rich manufacturing experience and many substantial factories which stable cooperated for many years, Mighty suppliers customers high-quality products at very competitive prices.
Customer’s satisfaction is our First Priority, We adhere to the concept of ” Quality First, Customer First”. We will continue to provide high-quality products and the best services to our customers and build up CZPT long-time friendship partners.
Our Advantages More than 20 years of manufacturing and exporting experience Packaging & Shipping FAQ 1. What’s the minimum order quantity? We don’t have the minimum order quantity. We can also provide free samples, but you need to pay the freight. Yes, we provide ODM&OEM services to customers around the world, and we can customize different brands and different sizes of packaging boxes according to customers’ requirements. We guarantee that our products will be free from defects in materials and workmanship within 12 months from the date of delivery. The warranty is void due to improper use, incorrect installation, and physical damage. 4. How to place an order? Send us an email of the models, brand, quantity, consignee information, model of transportation, and payment 5. What are your packing conditions? We use standardized export packaging and environmental protection packaging materials. If you have a legally registered patent, we will package the goods in your brand box after receiving your authorization 6. What are your payment terms? T/T is 30% of the payment in advance and 70% balance before delivery. Before you pay the balance, we will show you photos or videos of the products and packaging. 7. How long is your delivery time? The delivery time of sample order is 3-5 days, and that of a batch order is 5-45 days. The exact delivery time depends on the item and the quantity you ordered. 8. Do you test all products before delivery?
The 5 components of an axle, their function and installationIf you’re considering replacing an axle in your vehicle, you should first understand what it is. It is the component that transmits electricity from 1 part to another. Unlike a fixed steering wheel, the axles are movable. The following article will discuss the 5 components of the half shaft, their function and installation. Hopefully you were able to identify the correct axle for your vehicle. Here are some common problems you may encounter along the way. five componentsThe 5 components of the shaft are flange, bearing surface, spline teeth, spline pitch and pressure angle. The higher the number of splines, the stronger the shaft. The maximum stress that the shaft can withstand increases with the number of spline teeth and spline pitch. The diameter of the shaft times the cube of the pressure angle and spline pitch determines the maximum stress the shaft can withstand. For extreme load applications, use axles made from SAE 4340 and SAE 1550 materials. In addition to these 2 criteria, spline rolling produces a finer grain structure in the material. Cutting the splines reduces the strength of the shaft by 30% and increases stress. FunctionAxles play several important roles in a vehicle. It transfers power from the transmission to the rear differential gearbox and the wheels. The shaft is usually made of steel with cardan joints at both ends. Shaft Shafts can be stationary or rotating. They are all creatures that can transmit electricity and loads. Here are some of their functions. Read on to learn more about axles. Some of their most important features are listed below. MaterialThe material used to make the axle depends on the purpose of the vehicle. For example, overload shafts are usually made of SAE 4340 or 1550 steel. These steels are high strength low alloy alloys that are resistant to bending and buckling. Chromium alloys, for example, are made from steel and have chromium and molybdenum added to increase their toughness and durability. InstallThe process of installing a new shaft is simple. Just loosen the axle nut and remove the set bolt. You may need to tap a few times to get a good seal. After installation, check the shaft at the points marked “A” and “D” to make sure it is in the correct position. Then, press the “F” points on the shaft flange until the points are within 0.002″ of the runout.
China wholesaler Wheel Hub Bearing 512432, 2119810227, Br930813 with Best Sales
Product Description
Contact:; Joanna Xuan 2.;Product Specification:; 3.;About us :; Some New models of our wheel hub bearing,;Hub assembly as following:;
Screw Shaft TypesA screw shaft is a cylindrical part that turns. Depending on its size, it is able to drive many different types of devices. The following information outlines the different types of screws, including their sizes, material, function, and applications. To help you select the right screw shaft, consider the following factors: SizeA screw can come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from a quarter to a quarter-inch in diameter. A screw is a cylindrical shaft with an inclined plane wrapped around it, and its main function is to fasten objects together by translating torque into a linear force. This article will discuss the dimensions of screws and how to determine the size of a screw. It is important to note that screw sizes can be large and small depending on the purpose. MaterialThe material of a screw shaft plays an important role in the overall performance of a screw. Axial and central forces act to apply torque to the screw, while external forces, such as friction, exert a bending moment. The torsional moments are reflected in the torque, and this causes the screw to rotate at a higher rate than necessary. To ensure the longevity of the screw, the material of the screw shaft should be able to handle the bending moment, while the diameter of the shaft should be small enough to avoid causing damage. FunctionThe function of a screw shaft is to facilitate the rotation of a screw. Screws have several thread forms, including single-start, double-start and multi-start. Each form has its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article we’ll explore each of them in detail. The function of a screw shaft can vary based on its design, but the following are common types. Here are some examples of screw shaft types and their purposes. ApplicationsThe design of screws, including their size and shape, determines their critical rotating speeds. These speeds depend on the threaded part of the screw, the helix angle, and the geometry of the contact surfaces. When applied to a screw, these limits are referred to as “permissible speed limits.” These maximum speeds are meant for short periods of time and optimized running conditions. Continuous operation at these speeds can reduce the calculated life of a nut mechanism.
China Best Sales Bicycle 36 Hole Sealed Bearing Rear Hub wholesaler
Product Description
Bicycle 36 Hole Sealed Bearing Rear Hub Product Description
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
ZheJiang HongChi bicycle Co. Ltd located in the biggest bicycle accessory base. We get a wonderful geography, convenient We are professional manufacturer in producing chain wheel&crank, saddle, inner tube, tyre, pedal, front axle, rear axle, MTB bicycle, BMX bicycle, child toys, etc. branded “HongChi”. Meanwhile, we have the autonomy in operation of the import and Hard work and CZPT pursuit is our spirit. Quality first and customer first is our principle. Everyone in HongChi Company is sincerely inviting the colleague all over the world to have cooperation and a better future. Our Advantages 1. Manufacturer FAQ
An Overview of Worm Shafts and GearsThis article provides an overview of worm shafts and gears, including the type of toothing and deflection they experience. Other topics covered include the use of aluminum versus bronze worm shafts, calculating worm shaft deflection and lubrication. A thorough understanding of these issues will help you to design better gearboxes and other worm gear mechanisms. For further information, please visit the related websites. We also hope that you will find this article informative. Double throat worm gearsThe pitch diameter of a worm and the pitch of its worm wheel must be equal. The 2 types of worm gears have the same pitch diameter, but the difference lies in their axial and circular pitches. The pitch diameter is the distance between the worm’s teeth along its axis and the pitch diameter of the larger gear. Worms are made with left-handed or right-handed threads. The lead of the worm is the distance a point on the thread travels during 1 revolution of the worm gear. The backlash measurement should be made in a few different places on the gear wheel, as a large amount of backlash implies tooth spacing. Bronze or aluminum worm shaftsWhen selecting a worm, a few things should be kept in mind. The material of the shaft should be either bronze or aluminum. The worm itself is the primary component, but there are also addendum gears that are available. The total number of teeth on both the worm and the addendum gear should be greater than 40. The axial pitch of the worm needs to match the circular pitch of the larger gear. Calculation of worm shaft deflectionThe centre-line distance of a worm gear and the number of worm teeth play a crucial role in the deflection of the rotor. These parameters should be entered into the tool in the same units as the main calculation. The selected variant is then transferred to the main calculation. The deflection of the worm gear can be calculated from the angle at which the worm teeth shrink. The following calculation is helpful for designing a worm gear. Lubrication of worm shaftsIn order to protect the gears, worm drives require lubricants that offer excellent anti-wear protection, high oxidation resistance, and low friction. While mineral oil lubricants are widely used, synthetic base oils have better performance characteristics and lower operating temperatures. The Arrhenius Rate Rule states that chemical reactions double every 10 degrees C. Synthetic lubricants are the best choice for these applications.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||